1.1 The quality of male rabbits feeding semen is closely related to the nutrients in the feed. The breeding period should be fed with more feeds that are beneficial to sperm production, especially feeds containing vitamins such as barley malt, wheat sprouts, carrots, fish meal, and soy. Feed nutrition should be full price, especially protein, minerals, vitamins and other content should be appropriate. During the non-breeding period, moderate nutritional levels can be maintained. Normal summer and autumn day feeding amount, fine material 100 to 120 grams, grass 800 to 1000 grams. In winter and spring, the amount of concentrate is 100-120 grams, 150-200 grams of root and tuber, and 150-200 grams of hay. The composition of concentrated feed is cornmeal 27%, bean cake 25%, wheat bran 20%, barley 20%, fish meal 5%, shell powder 2%, salt 1%, plus multi-dimensional 0.05%. Body condition can not be too fat or too thin, moderate to upper sensation is appropriate. The male and female rabbits selected to be used for breeding should be kept separately when they are between 3 and 3.5 months of age to avoid early mating.
1.2 Management of Male Rabbits In order to make male rabbits strong in physique and strong in mating ability, exercise should be strengthened, and at least 1 to 2 hours of basket exercise every day. When mating, the female rabbit should be placed in a rabbit cage. It is not advisable to place the male rabbit in the female rabbit cage. The breeding frequency of male rabbits should be reasonable. It is advisable to use two times in one day. Young male rabbits can only be assigned one time in one day, and one day of breeding should be taken after two to three days of breeding. Breeding too early and too frequent will reduce the useful life of male rabbits. Generally, 1 male rabbit can be equipped with 8 to 10 female rabbits. The use of male rabbits for about three years should be eliminated in time.
Feeding and management of 2 female rabbits
2.1 The feeding and management of pregnant female rabbits The period from the end of mating to delivery is called gestation. During this period, the female rabbit needs to maintain its own life activities and provide nutrients for the growth and development of the fetus. Therefore, a large amount of nutrients is required throughout the pregnancy, especially in the latter part of pregnancy.
2.1.1 Breeding of pregnant female rabbits: According to the characteristics of the female gestation period, it is necessary to provide female rabbits with a high protein content feed, and also to supplement mineral and vitamin feeds. The daily feeding amount of feed also needs to increase. In summer and autumn, the daily feed amount of condiments is 130-150 grams, and grass is 1100-1300 grams. In winter and spring, the condiment feed amount is 130-150 grams, and the root and tuber types are 250-300 grams, hay is 200-300 grams. The composition of concentrated feed is: cornmeal 25%, soybean cake 25%, wheat bran 20%, barley 20%, fish meal 5%, shell powder 2%, salt 1%, edible sugar 2%, plus multi-dimensional 0.05%. During this period, the postpartum female rabbits have a good lactation ability, and they are well-developed and have a strong life force. It is forbidden to feed mildewed or deteriorated feedstuffs.
2.1.2 Management of pregnant female rabbits: Care should be taken to prevent miscarriage, premature birth and stillbirth. Take care when catching. The rabbit house must not be entered by keepers and keep quiet. Rabbit cages should be dry and warm water in winter. The litter preparation work must be done 2 to 3 days before the childbirth, and the rabbit cage and the litter box should be disinfected and rinsed with clean water. The disinfected crate was placed in a cage and clean hay was placed inside the crate.
2.2 Feeding and management of lactating female rabbits The period of time from the time that the female rabbit is weaned to the weaning of the pups is lactation. This period is generally 35 to 40 days. Throughout the lactation period, the female rabbits produce about 4 kg of milk.
2.2.1 Feeding of lactating female rabbits: The quality of the feed during this period will directly affect the milk yield and quality. Therefore, feeds rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals should be given. At the same time to give more fresh green, juicy feed, such as dandelion, plantain, bitter leeks and so on. In summer and autumn, the daily feed amount of condiments is 130-150 grams, and grass is 1200-1400 grams. In winter and spring, the daily feed amount of concentrates is 130-150 grams, and the root and tuber type is 260-300 grams; hay is 230-260 grams. The composition of concentrated feed is: cornmeal 20%, bean cake 25%, wheat bran 20%, rice bran 20%, barley 10%, fishmeal 4%, salt 1%, plus multi-dimensional 0.05%. The lactating female rabbits are fed 3 to 4 times a day. In addition, sufficient clean drinking water must also be provided.
2.2.2 Management of lactating female rabbits: Clean the rabbit house hygiene, clean the feeding trough, and replace the bedding every day. Within 3 days after giving birth, female rabbits were given 0.5 g of sulfathiazole and soda tablets each day to reduce the incidence of mastitis, sepsis and other diseases.
2.3 Feeding Management of Empty Breeding Rabbits This refers to the period of time before the puppies are weaned until they are mated again. This period is also called the resting period. Most of the females in this period are relatively thin, so we should restore our strength as soon as possible to lay a good foundation for the next mating. To do this, you should feed more high-quality green and blue succulent feeds and feed them properly. At the same time to prevent the female rabbit too fat or too thin. Over-fertilization affects the development of the female's egg cells; when it is too thin, the estrus is not normal.
3 Feeding and management of puppies
The puppies refer to rabbits from birth to weaning. The pups grow rapidly, but they have poor adaptability, weak disease resistance, susceptible to disease, and even death. For this reason, care should be taken carefully and carefully. According to its growth and development characteristics, it can be divided into the sleeping period and the open period.
3.1 Sleep period The period from birth to opening the eyes of a puppies is called the sleep period. This period should be as early as possible so that puppies can eat colostrum, and carefully managed. The lack of immune antibodies in pups born after birth must be obtained from colostrum. For this reason, it is important that the puppies eat colostrum as soon as possible. In addition, colostrum contains various nutrients necessary for the growth and development of puppies, which is very important for its growth and development and to enhance its viability. Newly born puppies only eat milk once a day, sleep after eating, and no excrement. Eat 2 times a day after 1 week. When the pups were full, they slept quietly, bulged in their abdomen, ruddy complexion and bright hair. When they were not full, the puppies were restless in the nest, crawled around, skin was shrunken, and the abdomen was slender and flat, and the skin was dark. The hair is dry and dull. Some mothers with weak motherhood, especially female rabbits, do not take care of the young rabbits after giving birth. They don't breast-feed while they are on the side, but they die when they are too long. Therefore, compulsory breastfeeding measures should be taken. The method is: let the female rabbit keep quiet, and make it fixed in the production box, will be placed on the female rabbit's nipple respectively to make it suck sucking milk, adhere to 4 to 5 times a day for 3 to 5 consecutive days, The female rabbit will automatically breastfeed.
The female rabbits die after giving birth or have insufficient milk after giving birth and suffer from diseases. They may seek foster mothers or receive artificial nursing. The method of fostering is as follows: first remove the pups from the production box, and divide the nest according to their size and strength. In order to prevent the female rabbits from being bitten or bitten by the foster female rabbits, the urine of the female rabbits is rubbed on the young rabbits, and the lactation status of the young ones is observed. It is found that the female rabbits have abandoned the rabbits and should be promptly removed and then fostered separately. . Manual feeding can be used glass dropper, syringe, should be boiled before use. Put a bicycle valve core hose on one end of the glass tube, artificial milk can be used milk, goat milk, etc., the concentration should be appropriate, after boiling disinfection cooling to 37 °C ~ 38 °C fed, 1 or 2 times a day, do not feed Urgent, eat enough.
In addition, newborn rabbits have poor adaptability to the external environment and weak resistance. Therefore, puppies should prevent cold in winter and prevent moisture in summer. To replace the grass mats in a timely manner, keep the box clean, soft and loose.
3.2 The eye-opening puppies begin to blink about 12 days after birth and are known as eye-opening periods from opening to weaning. Supplementary food is the focus of raising the eye opening period. After opening his eyes, the puppies are extremely active and scurry. As puppies grow older, breast milk has not been able to meet the needs of its growth and development. For this reason, when puppies are born from 16 to 18 days of age, they should be given supplements to puppies. Because puppies have poor digestion and fast growth, they should supply easily digestible and nutrient-rich feeds, such as the leaves of soya milk, milk, leguminous plants, or grasses, and they should also add appropriate amounts of minerals and vitamins. The number of feedings is 5-6 times a day, feeding less frequently and gradually increasing.
The pups should be weaned in time 35 to 45 days of age. Weaning prematurely affected the growth and development of young rabbits, and the survival rate of young rabbits was low. Weaning too late affects the female's health and the number of breedings each year.
In terms of management, the puppies should clean up the excrement in time and keep the crate clean. Always observe the health status of the pups. Do a good job of preparing the weaning rabbit's weaning nest. The cages, troughs, and water boxes needed should be cleaned and disinfected.
4 Feeding management of young rabbits
From weaning to 3 months old rabbits are called young rabbits. At this stage, the growth and development of young rabbits is fast, and because of the newly weaned, poor digestion, weak disease resistance and poor adaptability. Therefore, the following work should be done in feeding and management:
Feed more nutritious, digestible concentrates and supplement some animal feeds. Also feed some juicy green feed, such as pods, dandelions, etc. It is advisable to feed on a daily basis, feeding 3 to 5 times a day, feeding less frequently. Young rabbits are susceptible to enteritis, dermatitis, coccidiosis, etc. In the feed, about 0.3 grams of oxytetracycline and sulfonamides are often added. The cage should be placed in a sunny, leeward, dry place, so that the young rabbits receive more sunlight, but not easy to shine under strong light. In indoor breeding in winter, the temperature should be kept at 5°C~10°C, and at the same time, do a good job of indoor and cage care.
5 Feeding management of young rabbits
Young rabbits were termed 3 months or more to mature mating or commercial rabbits. It grows very quickly. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure adequate quality hay, green and juicy feed and mineral feed. The young rabbits are dominated by green roughage, but by the age of 3.5 months, the concentrate should be appropriately increased. In the summer and autumn, the daily feed amount is 40-70 grams, and the green feed is 600-700 grams. In winter and spring, the daily feed amount is 50-90 grams, 200 grams of roots, and 130-160 grams of hay powder. The ratio of concentrated feed: cornmeal 30%, soybean cake 20%, wheat bran 20%, rice bran 20%, barley 6%, fish meal 3%, salt 1%, fed 3 to 4 times a day.
In management, the group of rabbits, male and female should be kept separately, it is best to a rabbit cage, to prevent early allocation. At the age of 4.5 to 5 months, a thorough examination should be carried out and the breeding should be carried out. In accordance with the requirements of the rabbits, they should be placed in the breeding population to make a good lineage record. For male and female rabbits that have not reached the breeding standard, rabbits should be reared and fattened.
Intermediates of Cladribine, Carvedilol, Lurasidone, olmesartan, Risedronate Sodium, Atazanavir, Saxagliptin, Dabigatran,Dapoxetine,Cefixime,Ceftaroline fosamil and etc.
In the short span of time, we have emerged as most promising pharmaceutical intermediates manufacturers, chemical intermediates and bulk drug intermediates suppliers. Our consistent supply, quality products and dedication towards clients have opened up many international avenues for our growth.
In addition, the company also can follow the customer's product needs custom synthesis services
MAIN API PRODUCTS USP/BP
|
PRODUCT NAME |
CAS NUMBER |
SPEVIFICATION |
|
Azithromycin |
117772-70-0 |
BEP |
|
Cefpirome Sulphate sterile |
84957-29-9 |
USP JP16 |
|
Ceftriaxone Sodium (Sterile) |
104376-79-6 |
USP31 |
|
Cefotaxime |
64485-93-4 |
USP30 |
|
Ciprofloxacin HCL |
85721-33-1 |
USP/BP |
|
Gentamicin sulphate |
1405-41-0 |
BP |
|
Levofloxacin |
100986-85-4 |
USP27 |
|
Lincomycin Hydrochloride |
859-18-7 |
EP6.0 |
|
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride |
186826-86-8 |
USP31 |
|
Tigecycline |
220620-09-7 |
USP |
|
Linezolid |
165800-03-3 |
EP |
|
Dexamethasone |
50-02-2 |
USP/BP/EP |
|
Methylprednisolone |
83-43-2 |
USP/BP/EP |
|
Dexketoprofen trometamol |
156604-79-4 |
BP2008 |
|
Ibuprofen |
15687-27-1 |
BP |
|
Metamizol |
68-89-3 |
DAB |
|
Sulindac |
38194-50-2 |
USP/BP/EP |
|
Naproxcinod |
163133-43-5 |
USP28 |
|
Tripelennamine Hydrochloride |
154-69-8 |
USP28 |
|
Itraconazole |
84625-61-6 |
USP/BP |
|
Cytarabine |
147-94-4 |
USP31 |
|
Leucovorin Calcium |
1492-18-8 |
USP32 |
|
Valsartan |
137862-53-4 |
USP30 |
|
Telmisartan |
144701-48-4 |
USP31 |
|
Rosuvastatin Calcium |
147098-20-2 |
USP/BP |
|
Pitavastatin Calcium |
147526-32-7 |
USP/BP |
|
Fluvastatin |
93957-54-1 |
USP31 |
|
Vinpocetine |
42971-09-5 |
EP6.0 |
|
Atazanavir |
198904-31-3 |
BP |
|
Rosiglitazone |
122320-73-4 |
USP30 |
|
Esomeprazole Magnesium |
161973-10-0 |
USP/BP |
|
Topiramate |
97240-79-4 |
USP31 |
|
Fexofenadine HCl |
153439-40-8 |
Inhouse |
|
Bosentan |
147536-97-8 |
Inhouse |
|
D-Cysteine |
921-01-7 |
Inhouse |
|
D-Phenylalanine |
673-06-3 |
Inhouse |
|
Linagliptin |
668270-12-0 |
Inhouse |
|
Rivaroxaban |
366789-02-8 |
USP |
|
Saxagliptin |
361442-04-8 |
USP |
|
Vildagliptin |
274901-16-5 |
USP |
Major Pharmaceutical Intermediates
| Items Descripation | Structure | Application |
|
MICA ESTER CAS No: 246035-38-1 Purity: ≥98% |
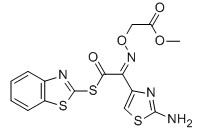 |
For Cefixime |
|
EHATA CAS No: 64485-82-1 Purity: ≥98% |
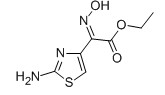 |
For Ceftazidine |
|
2-Chloroadenine CAS No: 1839-18-5 |
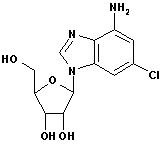 |
For Cladribine, Fludarabine et al |
|
Bicyclo(2,2,1)Heptane-2,3-di-exo-carboximide CAS No: 14805o-29-9 |
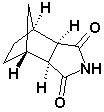 |
For Lurasidne |
|
(R,R)-1,2-Bis(methanesulfonyloxy methyl)Cyclohexane CAS No: 186204-35-3 |
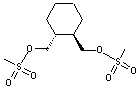 |
For Lurasidone |
|
3-(Piperazin-1-yl)benzol[d] isothiazole CAS No: 87691-87-0 |
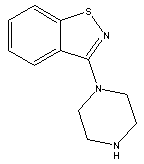 |
For Lurasidone |
|
Trityl olmesartan CAS No: 144690-92-6 Purity: ≥98% |
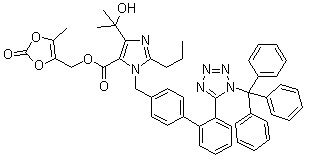
|
For olmesartan |
|
3-Acetyl Pyridine CAS No: 350-03-8 |
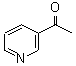
|
For Risedronate Sodium |
|
3-(AceticAcid)pyridine HCL CAS No: 6419-36-9 |
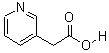 |
For Risedronate Sodium |
|
Risedronic Acid CAS No: 105462-24-6 |
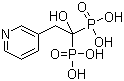 |
For Risedronate Sodium |
|
3-Hydroxy-1-adamantyl-D-Glycine CAS No: 709031-29-8 |
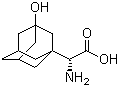 |
For Saxagliptin |
|
(1s,3s,5s)-3-(aminocarbonyl)-2-azabicyclo(3,1,0) hexane-2-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester CAS No: 361440-67-7 |
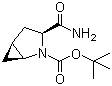 |
For Saxagliptin |
|
(S)-N-Boc-3- hydroxy-adamantylglycine CAS No: 361442-00-4 |
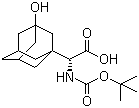 |
For Saxagliptin |
|
2-Azabicyclo[3.1.0] hexane-3-carbonitrile, (1s,3s,5s)- CAS No: 866083-42-3 |
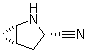 |
For Saxagliptin |
|
Ethyl 3-(pyridin-2-ylamino) propanoate CAS No: 103041-38-9 |
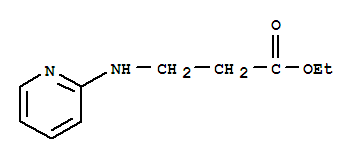 |
For Dabigatran |
|
N-(4-Cyanophenyl) glycine CAS No: 42288-26-6 |
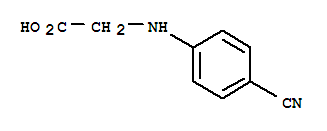 |
For Dabigatran |
|
4-methylamino-3-nitrobenzoic Acid CAS No: 41263-74-5 |
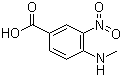 |
For Dabigatran |
|
S-3-Amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid ethyl ester HCL CAS No: 167834-24-4 |
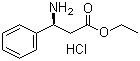 |
For Dapoxetine |
|
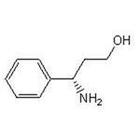
(S)-3-Amino-3-Phemylpropan -1-ol CAS No: 82769-76-4 |
|
For Dapoxetine |
|
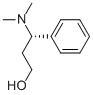
(S)-3-Dimethylamino-3-Phemylpropanol CAS No: 82769-75-3 |
|
For Dapoxetine |
|
4-{4-[4-(hydroxydiphenylmethyl)-1-piperidinyl]-1-butynil}-α,α-dimethyl benzene acetic acid CAS No: 832088-68-3 |
For Fexofenadine HCl | |
|
Methyl 2-(4-(4-chlorobutanoyl)phenyl)-2-methylpropanoate CAS No:154477-54-0 |
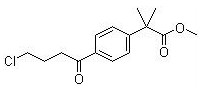
|
For Fexofenadine HCl |
|
5-Bromo-2-chlorophenyl)(4-ethoxyphenyl)methanone CAS No 461432-22-4 |
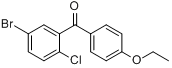
|
For Dapagliflozin |
|
4-(5-Bromo-2-chlorobenzyl)phenyl ethyl ether CAS No :461432-23-5 |
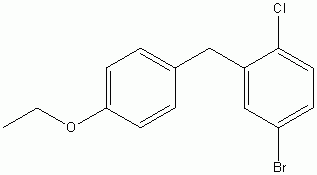
|
For Dapagliflozin |
Mica Ester,Pharma Intermediates,Ciprofloxacin Hcl Uses,Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
NINGBO VOICE BIOCHEMIC CO. LTD , https://www.pharma-voice.com