The stalks of the melon vines are very strong. On the mother vines, the vines grow, and on the vines, the vines are born. If left to grow, usually the growth of most female vines is very weak, while the growth of vine vines and vine vines is very strong. Most of the female flowers are grown on Ziman and Sun vines. A very small number of female flowers can also be found in the leaves of the main vine at low temperatures.
Due to the small space in the greenhouse and the high density of cultivation, it is necessary to fully utilize the space in the greenhouse to obtain ideal ventilation and light conditions for melon, and to obtain high yield and excellent quality of melon. The melon plants in the shed must be pruned.
The pruning includes topping the mother vine, the vine, and the cranberry, or removing the excess vine, leaving the vine, leaving the leaves, and removing the tendrils.
The main purpose of pruning is to artificially regulate the growth of plants. The leaves are the organ of nutrient production, but excessive stems and leaves will consume nutrients and affect fruit development. By pruning, the vegetative body can be maintained in an appropriate size, and the yield and quality of the fruit will not be affected by too many or too few stems and leaves; the second is to promote flowering and fruit setting and achieve early maturation and high yield; and secondly, to regulate the distribution of nutrients. At the seedling stage (4 to 5 true leaves), the nutrient is transferred to the lateral branch in time to promote lateral branching. When the fruit on the branch is seated, the resulting shoots are toned in time, so that the nutrients can be transported to the fruit and can prevent the melon , promote fruit enlargement.
Many melon pruning methods should be combined with the characteristics of varieties, cultivation methods, soil fertility, and the number of melons to be determined, greenhouses commonly used in the cultivation of thick single melon pruning and double vine pruning, greenhouse thinning melon cultivation with three vine pruning.
(1) single vine pruning: It can be divided into female vines as the main vine single pruning and sub-ranch as the main vine single pruning. The mother vine is the main sinensis pruning, and it is the mother seedling that does not pick up the heart, and sits on the vine of a certain node and removes all the other vines. The single vine is the single vine pruning and is the mother. When vines have 4 to 5 pieces of real leaves, they pick their hearts and promote the growth of their sons. At the base, they choose to keep a sturdy vine, remove the rest of the vines, and use the vines to sit on them. When the seed vine is pruned, the lateral buds on the basal vines from 1 to 10 knots are all wiped out at the time of germination. Only the lateral vines that were born on the 11th to 15th nodes are selected. When the female vine is the main vine pruning, it is better to leave melons in the 14th-16th section in the spring, and it is better for the large-middle and late-maturing cultivars to get the results from 15-17 knots. Branches to the female flowers without fail. The main vine grows to 22 to 28 leaves when it is topped. If it adopts multi-level cultivation, it can leave one side bud at the top of the main vine, and all the side vines that do not have melons are wiped off.
(2) Double vine pruning: When the mother vines 4 to 5 true leaves topping, promote hair vines, from which to choose good growth, the site of the appropriate two sub-vines to leave, let it grow, wipe off the vine base 1 to 6 section The Sun vines (side buds) produced on the bit, choose Sun Man sitting on the 7th to 11th branches of the vine, and the Sun Man of the female flowers left 1-2 leaves topping. The Sun Man without the female flowers also wiped off when the buds sprouted. Each sapling is topped when it grows to 20 leaves, and two squash are left per plant. The double-cropping and pruning method has a high yield and is suitable for cultivation in the spring and autumn of large arch sheds, but the melon ripening period is later, and the ripening period is not too concentrated.
(3) three vine pruning: the main vines 5 to 6 leaves topping, choose to stay in the suitable three vines, sub-vines 6 to 8 leaves topping, Sun vines in female flowers 2 to 3 leaves topping, such as intensive foliage, can be removed as appropriate The results of the Sun Man, left 50 leaves per plant. Last to leave 2 to 3 melons, this method is mostly used for cultivation of thin-walled melons.
Regardless of the method adopted, the following issues should be taken into account when pruning: pruning should ensure that the stems and leaves are distributed reasonably and evenly to prevent stems and leaves from being closed, so as to make full use of the principle of land and solar energy. Stem vigorous growth period in time to pruning and vine, vine spread to the rapid expansion of the fruit is the vine vigorous growth period. The growth of stalks can reach 9-14 cm in one day. The stalks must be pruned in time for the rapid extension of the vines, and the seeds should be picked in time after being pollinated to promote the growth of the melons and fruits. The pruning should be carried out after 10 o'clock in the morning on sunny days. The pruning in rainy days or in the morning due to the humidity in the shed is not easy to heal, and it is easy to cause the infection. In addition. In the morning, the vines are brittle, easily broken, and other vines are easily damaged when the twigs are trimmed. Pruning should ensure that there are more functional leaves in fruit enlargement and maturity. The leaves are the organs that make nutrients. The melon leaves produce more nutrients at about 30 days of age, and most of the nutrients are supplied to other parts of the plant. At this time, the leaves are either young leaves or functional leaves. When the fruit is enlarged, the more functional leaves, the more nutrients are supplied to the fruit. It is not premature to pick up the side vines. Because the growth of the plant roots depends on the supply of leaf nutrients, it is appropriate to remove the collaterals late to promote root development. The production can be picked up when the side branches grow to 4 to 5 cm. For side vines sitting on melons, leave 1 to 2 leaves topping before melons.
When contemplating a conservatory in a solar greenhouse (ie, a winter greenhouse), a 10th iron wire may be fixed in the east-west direction at a distance of 2 to 2.2 meters from the ground at the rear pillar, and a 10th wire may be fixed at the near-top end of the front pillar. According to the direction of the cultivation line (north-south direction), one line of 16-18 iron wire is fixed in each row, and the two ends are respectively tied to the iron wires of the front and rear columns. Generally use nylon rope or plastic rope hanging. The sling can be tied directly to the bottom of the plant, and the melon vines and slings can be entangled. The method of fixing the wire and nylon rope in the arched circular greenhouse can refer to the fixing method of the winter warm greenhouse. Generally when the vine grows 40 centimeters, it should be condolenced, and with the growth of the plant, the stem vines will be properly wrapped.
Brackets and tied vines Because bamboo vines and nylon ropes are not easy to swing, they are easy to hang, and can prevent melons and other advantages, so bamboo rakes can be used as scaffolds in melon cultivation. Generally choose thick bamboo thumb, the length according to the height of the greenhouse, usually 2.2 to 2.5 meters. Before the melon dumping vines, the racks can be used. About 10 centimeters from the base of the plant, along the direction of the melon line, each plant inserted a bamboo pole, requiring the firmness of the plug, plug upright, so that each line is a straight line. A bamboo pole is horizontally and laterally fixed at 80 cm from the ground and 20 cm from the top of the bamboo pole, or the pole is fixed at the wire along the planting line, so that the bamboo pole does not have to be tied horizontally at the top. If it is not fixed between the rows of wire, then in the vertical direction with the melon row, the bamboo poles are used as tie rods to connect the rows of standing poles together. The tie rods are fixed on a cross ridge at the top of the vertical pole, and the rows can be arranged. The crossbars are fastened on a scaffold, which prevents the melons from becoming slanted or collapsed when they grow.
After the vine spreads, the melon vines are led to the vertical pods in a timely manner, and the vines are fixed to the rakes with the “8â€-shaped rope ties. Before the seedlings grow to the first horizontal crucible, they are tied first. After the seedling grows to the first cross, the crucible grows and grows in the same direction on the horizontal crucible. After it grows to a certain extent, it leads to Liying. Continue to grow upwards. When tying the vines, care must be taken not to break tender stems, leaves, female flowers, fruits, etc., and pay attention to vines so that leaves and melons can be properly distributed in space.
Due to the small space in the greenhouse and the high density of cultivation, it is necessary to fully utilize the space in the greenhouse to obtain ideal ventilation and light conditions for melon, and to obtain high yield and excellent quality of melon. The melon plants in the shed must be pruned.
The pruning includes topping the mother vine, the vine, and the cranberry, or removing the excess vine, leaving the vine, leaving the leaves, and removing the tendrils.
The main purpose of pruning is to artificially regulate the growth of plants. The leaves are the organ of nutrient production, but excessive stems and leaves will consume nutrients and affect fruit development. By pruning, the vegetative body can be maintained in an appropriate size, and the yield and quality of the fruit will not be affected by too many or too few stems and leaves; the second is to promote flowering and fruit setting and achieve early maturation and high yield; and secondly, to regulate the distribution of nutrients. At the seedling stage (4 to 5 true leaves), the nutrient is transferred to the lateral branch in time to promote lateral branching. When the fruit on the branch is seated, the resulting shoots are toned in time, so that the nutrients can be transported to the fruit and can prevent the melon , promote fruit enlargement.
Many melon pruning methods should be combined with the characteristics of varieties, cultivation methods, soil fertility, and the number of melons to be determined, greenhouses commonly used in the cultivation of thick single melon pruning and double vine pruning, greenhouse thinning melon cultivation with three vine pruning.
(1) single vine pruning: It can be divided into female vines as the main vine single pruning and sub-ranch as the main vine single pruning. The mother vine is the main sinensis pruning, and it is the mother seedling that does not pick up the heart, and sits on the vine of a certain node and removes all the other vines. The single vine is the single vine pruning and is the mother. When vines have 4 to 5 pieces of real leaves, they pick their hearts and promote the growth of their sons. At the base, they choose to keep a sturdy vine, remove the rest of the vines, and use the vines to sit on them. When the seed vine is pruned, the lateral buds on the basal vines from 1 to 10 knots are all wiped out at the time of germination. Only the lateral vines that were born on the 11th to 15th nodes are selected. When the female vine is the main vine pruning, it is better to leave melons in the 14th-16th section in the spring, and it is better for the large-middle and late-maturing cultivars to get the results from 15-17 knots. Branches to the female flowers without fail. The main vine grows to 22 to 28 leaves when it is topped. If it adopts multi-level cultivation, it can leave one side bud at the top of the main vine, and all the side vines that do not have melons are wiped off.
(2) Double vine pruning: When the mother vines 4 to 5 true leaves topping, promote hair vines, from which to choose good growth, the site of the appropriate two sub-vines to leave, let it grow, wipe off the vine base 1 to 6 section The Sun vines (side buds) produced on the bit, choose Sun Man sitting on the 7th to 11th branches of the vine, and the Sun Man of the female flowers left 1-2 leaves topping. The Sun Man without the female flowers also wiped off when the buds sprouted. Each sapling is topped when it grows to 20 leaves, and two squash are left per plant. The double-cropping and pruning method has a high yield and is suitable for cultivation in the spring and autumn of large arch sheds, but the melon ripening period is later, and the ripening period is not too concentrated.
(3) three vine pruning: the main vines 5 to 6 leaves topping, choose to stay in the suitable three vines, sub-vines 6 to 8 leaves topping, Sun vines in female flowers 2 to 3 leaves topping, such as intensive foliage, can be removed as appropriate The results of the Sun Man, left 50 leaves per plant. Last to leave 2 to 3 melons, this method is mostly used for cultivation of thin-walled melons.
Regardless of the method adopted, the following issues should be taken into account when pruning: pruning should ensure that the stems and leaves are distributed reasonably and evenly to prevent stems and leaves from being closed, so as to make full use of the principle of land and solar energy. Stem vigorous growth period in time to pruning and vine, vine spread to the rapid expansion of the fruit is the vine vigorous growth period. The growth of stalks can reach 9-14 cm in one day. The stalks must be pruned in time for the rapid extension of the vines, and the seeds should be picked in time after being pollinated to promote the growth of the melons and fruits. The pruning should be carried out after 10 o'clock in the morning on sunny days. The pruning in rainy days or in the morning due to the humidity in the shed is not easy to heal, and it is easy to cause the infection. In addition. In the morning, the vines are brittle, easily broken, and other vines are easily damaged when the twigs are trimmed. Pruning should ensure that there are more functional leaves in fruit enlargement and maturity. The leaves are the organs that make nutrients. The melon leaves produce more nutrients at about 30 days of age, and most of the nutrients are supplied to other parts of the plant. At this time, the leaves are either young leaves or functional leaves. When the fruit is enlarged, the more functional leaves, the more nutrients are supplied to the fruit. It is not premature to pick up the side vines. Because the growth of the plant roots depends on the supply of leaf nutrients, it is appropriate to remove the collaterals late to promote root development. The production can be picked up when the side branches grow to 4 to 5 cm. For side vines sitting on melons, leave 1 to 2 leaves topping before melons.
When contemplating a conservatory in a solar greenhouse (ie, a winter greenhouse), a 10th iron wire may be fixed in the east-west direction at a distance of 2 to 2.2 meters from the ground at the rear pillar, and a 10th wire may be fixed at the near-top end of the front pillar. According to the direction of the cultivation line (north-south direction), one line of 16-18 iron wire is fixed in each row, and the two ends are respectively tied to the iron wires of the front and rear columns. Generally use nylon rope or plastic rope hanging. The sling can be tied directly to the bottom of the plant, and the melon vines and slings can be entangled. The method of fixing the wire and nylon rope in the arched circular greenhouse can refer to the fixing method of the winter warm greenhouse. Generally when the vine grows 40 centimeters, it should be condolenced, and with the growth of the plant, the stem vines will be properly wrapped.
Brackets and tied vines Because bamboo vines and nylon ropes are not easy to swing, they are easy to hang, and can prevent melons and other advantages, so bamboo rakes can be used as scaffolds in melon cultivation. Generally choose thick bamboo thumb, the length according to the height of the greenhouse, usually 2.2 to 2.5 meters. Before the melon dumping vines, the racks can be used. About 10 centimeters from the base of the plant, along the direction of the melon line, each plant inserted a bamboo pole, requiring the firmness of the plug, plug upright, so that each line is a straight line. A bamboo pole is horizontally and laterally fixed at 80 cm from the ground and 20 cm from the top of the bamboo pole, or the pole is fixed at the wire along the planting line, so that the bamboo pole does not have to be tied horizontally at the top. If it is not fixed between the rows of wire, then in the vertical direction with the melon row, the bamboo poles are used as tie rods to connect the rows of standing poles together. The tie rods are fixed on a cross ridge at the top of the vertical pole, and the rows can be arranged. The crossbars are fastened on a scaffold, which prevents the melons from becoming slanted or collapsed when they grow.
After the vine spreads, the melon vines are led to the vertical pods in a timely manner, and the vines are fixed to the rakes with the “8â€-shaped rope ties. Before the seedlings grow to the first horizontal crucible, they are tied first. After the seedling grows to the first cross, the crucible grows and grows in the same direction on the horizontal crucible. After it grows to a certain extent, it leads to Liying. Continue to grow upwards. When tying the vines, care must be taken not to break tender stems, leaves, female flowers, fruits, etc., and pay attention to vines so that leaves and melons can be properly distributed in space.
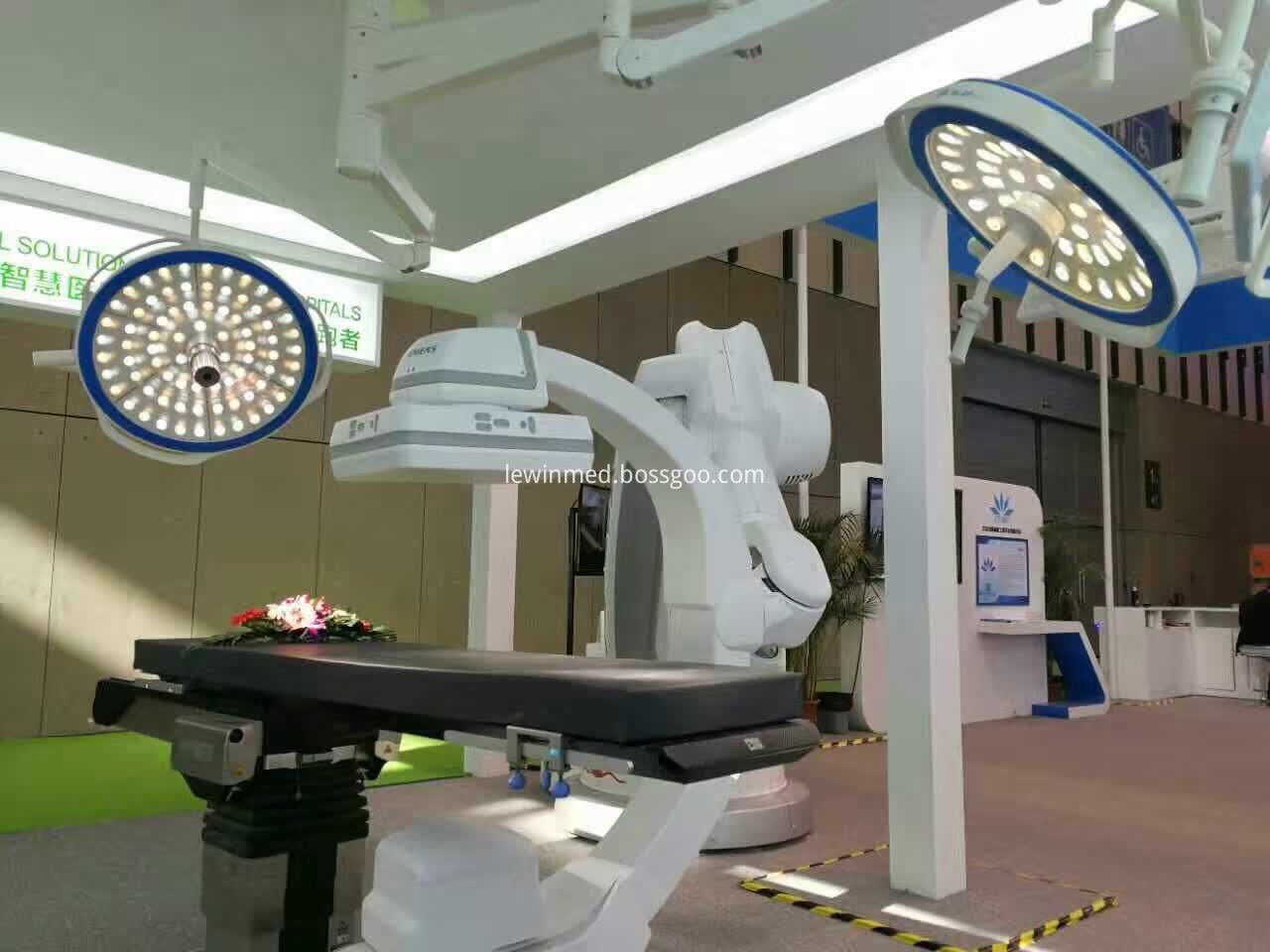
The double dome LED Surgical Lamp adopt the new type LED cold illuminant as the illumination source of operating lamps, it is not only benefit for the rapid recovery of surgery illuminate parts, but also improved the doctors' working environment and efficiency extremely; the operation lamp adopts LED as the light source of shadowless surgical lamps, energy-saving effect is remarkable, besides it's energy consumption only be the one tenth of general inscandescent light, one second of halogen lamp;

Double Dome Surgical Lamp,Double Dome Operation Light,Double Dome Surgery Lamp,Double Dome Operating Lamp
Shandong Lewin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.operatinglight.nl