Roughage generally refers to plant feeds with high crude fiber content and low nutritional value, such as crop straws, leaves, hay, shell awns, glutinous rice pods, and soybean meal. These feeds are coarse in texture, large in size, poor in palatability, and non-digestible, but generally contain more minerals, which have a good effect on promoting the development of bones in livestock and poultry. The proper processing and modulation of roughage for feeding livestock and poultry will not only be tolerant to hunger and diarrhea, but also an effective way to promote grain-saving and increase efficiency in the aquaculture industry.
1. Long straw short feed. As the saying goes: “The three grasses are not enough, and they have not been picked up.†Feeding the forage grasshoppers for a short period of time generally saves about 20%, the utilization rate increases by about 15%, and many feeds are eaten by the livestock during the whole feeding period. The hard-to-eat stalks can be used effectively for a short period of time, and the digestibility is also improved. Generally, the stalks fed to the cattle can be quailed to 4 to 6 cm, and the sheep can be bred to be shorter.
2. Fine grass feed. The smashing of the seeds or stalks by mechanical means facilitates the feeding and digestion of the livestock and facilitates the mixing of the digestive juice with the chyme, thereby reducing the energy consumption in the gastrointestinal digestion process and improving the utilization of the feed.
3. Hard grass soft feed. The stems, leaves, and seeds of forage grasses, after salting, saccharification, ammoniation, or microbial fermentation, can greatly improve their palatability and facilitate digestion and absorption.
4. A reasonable match. The first is with the thickness. Feeding raw forage grass first, the livestock are hungry, can eat more roughage, and then feed the concentrate or high-quality pasture according to their nutritional requirements. In this way, not only forage can be saved, but also the utilization of roughage by ruminant livestock can be fully utilized. Followed by the rough match. The general vitamin content of roughage is small. Feeding livestock and poultry with roughage should pay attention to the appropriate feeding of some green and juicy feeds and germinating feeds. The final is a rough match. When feeding the livestock and poultry with roughage, it is necessary to pay attention to reasonable adjustments and use, and strive to diversify. Do not feed one species for a long time. Otherwise, it will not only fail to meet the nutritional needs of livestock and poultry, but also cause disease. For example, long-term feeding of livestock with wheat straw can cause rumen retardation in cattle and sheep and dyspepsia in horses.
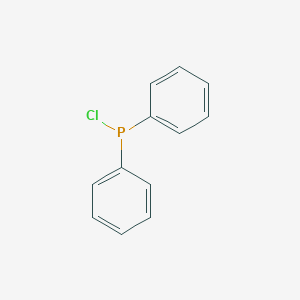
Chlorodiphenylphosphine CAS No.1079-66-9
Chlorodiphenylphosphine Basic Information
Product Name: Chlorodiphenylphosphine
CAS: 1079-66-9
MF: C12H10ClP
MW: 220.63
EINECS: 214-093-2
Mol File: 1079-66-9.mol
Chlorodiphenylphosphine Structure
Melting point 14-16°C
Boiling point 320 °C(lit.)
density 1.229 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
storage temp. Store at R.T.
solubility Miscible with alcohol. Slightly miscible with ammonia.
form Liquid
color Colorless to yellow
Water Solubility Reacts violently
Sensitive Air & Moisture Sensitive
Chlorodiphenylphosphine Application
Chlorodiphenylphosphine is used to introduce the diphenylphosphinyl moiety by aryl ortho-lithiation. It is also used as an intermediate to make antioxidants, flame retardants, stabilizers, catalysts, photoinitiators, and optical brighteners. Used as a halogenation reagent for the conversion of alcohols into halides, in the preparation of solid-phase reagent for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides.
Chlorodiphenylphosphine,Chlorodiphenylphosphine Oxide,Chlorodiphenylphosphine 31P Nmr,Chlorodiphenylphosphine Synthesis
ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com