--- Wang Wei Waters Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Protein glycosylation is one of the most important post-translational modifications of the life system and plays an important role in life processes such as immune recognition, protein secretion, and signal transduction. Polysaccharides linked to proteins are important carriers of these functions, especially for monoclonal antibody drugs, which have an important effect on the biological activity of the drug. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop a glycosylation analysis method with high separation efficiency and good detection sensitivity for the analysis of monoclonal antibody drugs.
In response to the difficulties in glycosylation analysis, Waters has developed hydrophilic interaction chromatography and fluorescence-mass spectrometry combined detection methods. The ACQUITY UPLC System works with fluorescence detectors (FLR) and polysaccharide analysis (GST) columns for higher resolution than HPLC methods. The dedicated column for polysaccharide analysis is packed with a 1.7 μm amide sorbent to efficiently separate fluorescently labeled polysaccharides in HILIC mode. UPLC with Fluorescence Detector® for the analysis of polysaccharides provides high resolution and quantitative accuracy, especially for positional isomers and small peaks with co-elution; mass spectrometry provides more structure for sugar chain identification information. By comparing with the retention time of standard sugar chains, the process can achieve high-throughput quantitative determination of polysaccharides to meet the diverse needs of drug analysis.
I. Chromatographic conditions and separation of labeled polysaccharide samples
The 2-AB labeled polysaccharide mixture can be efficiently separated by the HILIC method. For method optimization, a slower gradient is used to effectively improve the separation between adjacent glycan peaks at retention times; for other parameters such as flow rate, buffer concentration, mobile phase pH, and column temperature, etc. It also needs to be optimized. Figure 1 shows that after the optimized HILIC chromatographic conditions, the complex 2-AB labeled IgG polysaccharide mixture was well separated, including E1/E2 and F1/F2. The gradient elution time used in the experiment was 45 minutes, including column cleaning and re-equilibration steps. In general, the total analysis time for a sample is within 1 hour. Therefore, the UPLC chromatographic method using a 1.7-μm filler provides better separation and shorter run times than the HPLC method using a 3.0-μm filler. A 2.1 x 150 mm column was used in the experiment. In Figure 1 (B), mannose 5 (peak C) and mannose 6 (peak H) can be successfully separated from adjacent polysaccharide peaks, solving the problem of co-elution.
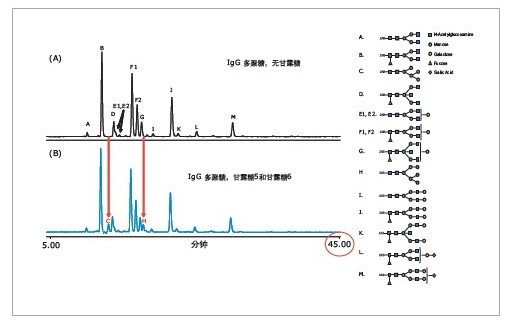
2. Quantification and structural identification of 2-AB labeled polysaccharides
Since the polysaccharide can achieve baseline separation in the HILIC mode, various isomers, such as the positional isomerism of the terminal sialic acid, can be well separated. Therefore, peak area integration under the fluorescence detector enables quantitative analysis of various sugar chains. From the MS spectrum, the proportion of high mannose glycoforms in polysaccharide samples is higher, and the composite and heterozygous sugar chains can also be identified. Various sugar chains with neuraminic acid can also be identified, indicating that the method can be adapted to the analysis of various polysaccharide complexes. In addition to the molecular weight, we can further confirm the structure of the polysaccharide by MS/MS spectrum.

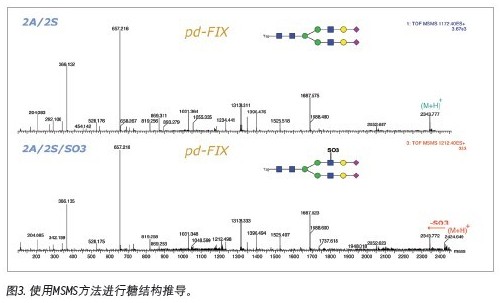
The results of the analysis of the 2-AB-labeled IgG polysaccharide mixture fully demonstrate that Waters provides a mature glycan analysis protocol, and the quality control of the corresponding column is performed using a 2-AB-labeled IgG polysaccharide mixture. The ACQUITYUPLC system significantly reduces analysis time by reducing the separation gradient that takes 2 hours or even 3 hours on conventional HPLC to 1 hour. In addition, Waters provides UPLC-FLR-MS's overall solution for efficient analysis of polysaccharides. In addition to providing molecular weight information, sugar structure derivation can be performed, which greatly reduces glycosylation analysis in biopharmaceutical research and development. Difficulty.
experiment process:
1. 2-AB labeled sugar chain
Using GlycoPro le kit, Prozyme
When using the kit for 2-AB-labeled sugar chains, follow the company's instructions in addition to the following steps.
1. Use 50 μl of labeled reaction solution
2. 65 degree reaction 4-5 hours
3. Dispose of the sample in step 4 to remove excess labeling reagent
Use Sigma reagent
1. Prepare 30% acetic acid DMSO solution (30 μl glacial acetic acid, 700 ul DMSO)
2. Prepare 2-AB solution in a ratio of 20:1 (v/w) (if 20 mg 2-AB is required, prepare with 400 μl 30% acetic acid DMSO solution)
3. Mixing the 2-AB solution with sodium cyanoborohydride in a ratio of 16.7:1 (v/w) to prepare a labeling reaction solution
4. The obtained sugar chain was dissolved in 50 μl of the labeled reaction solution, and the 65-degree shock was reflected for 4-5 hours.
5. The reaction solution is treated in step 4 to remove excess labeling reagent.
Second, use MassPrep hydrophilic action sample processing plate to remove excess labeling reagent
Required solution: MiniQ pure water, 90% acetonitrile ACN, 10 mM ammonium acetate Tris, 20% ACN
1. The sample processing plate is activated. Add 200 μl of MiniQ pure water to the sample processing plate, add 200 μl of 90% ACN, and repeat 90% ACN.
2. Pipette 50μl of labeling solution and add 450μl ACN (if there is sediment, do not centrifuge, so as not to reduce the recovery of sugar chain). Since the volume of each well on the plate is 200μl, the sample can be divided into four parts.
3. Add the sample to the treatment plate and set the vacuum to a low pressure (pressure 250-500 mmHg) to ensure sufficient time interaction between the sample and the HILIC matrix; if the solution does not move on the plate, increase the vacuum appropriately.
4. Clean the plate twice with 90% ACN
5. Replace the sample collection plate with 200 μl of 10 mM ammonium acetate Tris, 20% ACN, and transfer the eluate to a 1 ml centrifuge tube.
6. After lyophilization, the lyophilized sample of the sugar chain solution was redissolved in 20 μl of 50% ACN, and after 5 min of ultrasound, it was transferred to a UPLC sampling bottle and injected into 5 μl.
references
(1) Martin Gilar, Ying-Qing Yu, Joomi Ahn, and Hongwei Xie. Analysis of Glycopeptide Glycoforms in Monoclonal Antibody TrypticDigest using a UPLC HILIC Column
(2) Hongwei Xie, Weibin Chen, Martin Gilar, St John Skilton and Jeffery R. Mazzeo. Separation and Characterization of N-linked Glycopeptides on Hemagglutinins In A Recombinant Influenza Vaccine
(3) Joomi Ahn, Ying Qing Yu and Martin Gila.r UPLC Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC)-Fluorescence Detection for Analysis of 2-AB Labeled Polysaccharides
Anorectal Surgery Support,Sacrum Surgery Support,Operating Support Frame,Urology Surgery Accessories
NINGBO TECHART MEDICAL EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD , https://www.techartmed.com