Recently, the Suzhou Medical Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the research team of the Lishui Central Hospital and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Suzhou University have launched a new study.

The results of the study show that SE-DenseNet, an artificial intelligence system used in conjunction with medical imaging, combined with enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, can complete cancer grading for patients under non-invasive conditions. The research team said that the technology will be applied to the development of the liver cancer ablation planning navigation system to more accurately assist in the development of surgical planning.
Liver cancer and cancer grading
In primary liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an important type of liver cancer, accounting for 70% to 90% of primary liver cancer, and is the third largest cancer causing cancer death worldwide.
The classification of liver cancer has important clinical significance for the clinical diagnosis, treatment options and prognosis of patients.
Unlike most tumors, liver cancer can be diagnosed by non-invasive imaging. At present, the methods for diagnosing liver cancer include imaging examination, biopsy, and AFP serum examination. The most commonly used medical imaging examinations include CT and MR. CT and MR have been recognized as the first choice for non-invasive examination of diseases such as hepatobiliary and breast cancer.
Pathological biopsy is still a necessary means to assess the degree of malignancy of the lesion. If the medical imaging-based lesion classification can be achieved, it can provide a reference to the treatment plan of the tumor to a certain extent, which can reduce the dependence of the diagnosis on the pathological biopsy and greatly reduce the suffering of the patient.
However, in clinical applications, the grading results are highly dependent on the doctor's experience and have greater subjectivity. Therefore, seeking an objective and effective grading assessment method is an important research direction.
With the continuous development of technologies such as pattern recognition, machine learning and deep learning, the use of medical image-assisted diagnosis system to construct a deep learning network model and objective and automatic grading of liver cancer has become one of the mainstream research directions.
AI is a non-invasive classification of liver cancer patients
Researcher Dai Yakang, Researcher Zhou Zhiyong and Zhou Qing from the Suzhou Medical Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with the team of Associate Dean Ji Jiansong from Lishui Central Hospital and Fan Guohua, the second affiliated hospital of Suzhou University, proposed the SE-DenseNet network and developed an image based on enhanced MR ( Graded studies on the malignant degree of hepatocellular carcinoma with a layer thickness ranging from 3 mm to 8 mm.
Lei Feng.com learned that the study obtained enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of 75 patients from Lishui Central Hospital and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Suzhou University, including 75 arterial phase images, 75 venous images, and 63 delayed images. 213 lesions ROI.
By combining the DenseNet and Senet network structures in deep learning, the researchers built the SE-DenseNet network and used SEEND to weight the features for self-learning to achieve the enhancement of important features. To a certain extent, SE-DenseNet It relieves the feature redundancy of DenseNet.
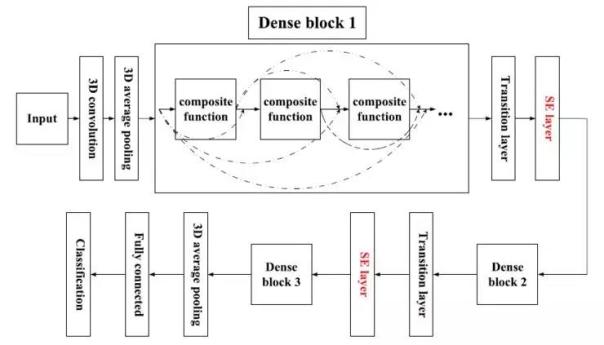
SE-DenseNet framework diagram
The experimental results show that the classification performance of SE-DenseNet is better than DenseNet and DenseNet-BC (SE-DenseNet:accuracy=0.83, DenseNet:accuracy=0.72, DenseNet-BC:accuracy=0.66).
The researchers said that the artificial intelligence system SE-DenseNet used in conjunction with medical imaging combined with enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance imaging can complete cancer grading for patients under non-invasive conditions. In the future, this technology will be applied to the development of the liver cancer ablation planning navigation system to more accurately assist in the development of surgical planning.
Zhou Zhiyong, a researcher at the Suzhou Medical Institute who participated in the study, said, "Compared to traditional cancer grading by puncture, the use of 'medical imaging + AI' grading can more comprehensively acquire lesion information and reduce the probability of missed detection. In recent years, The accuracy of using artificial intelligence for lesion grading is still increasing, indicating that this technology has broad prospects for disease diagnosis and treatment."
In addition, Lei Feng.com learned that the research has also received funding from the National Key R&D Program, Zhejiang Key R&D Program and Suzhou Citizen Technology.
Source: Lei Feng Net
Guangzhou Zhongzhinan Supply Chain Co.,Ltd. , https://www.gzzhongzhinan.com